In moment’s tech world, two places frequently get compared because both contribute heavily to structure and delivering ultramodern operations Full Stack Developers and DevOps Engineers. While both work nearly with development and deployment processes, their liabilities, chops, and diurnal tasks differ significantly.
Still, this companion will help you understand the difference between a Full Stack Developer and a DevOps Engineer in a simple and structured way, If you’re considering a career in IT but are doubtful which direction fits you better.
What Does a Full Stack Developer Do?
A Full Stack Developer works on both the frontal end and aft end of a software operation. This means they understand everything related to the stoner interface, garçon sense, databases, and APIs.
Their thing is to make complete, functional operations from launch to finish. Full Stack Developers frequently work nearly with contrivers on one side and DevOps or deployment brigades on the other.
Full Stack Developers generally work with:
- Frontend technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, Angular, etc.)
- Backend fabrics (Node.js, Python Django, Java Spring Boot, etc.)
- Databases (MySQL, MongoDB, PostgreSQL)
- API design and integration
- Basic cloud services
They’re problem-solvers who move between multiple places to produce responsive, dependable, and stoner-friendly operations.
What Does a DevOps Engineer Do?
DevOps Engineers concentrate on structure, automating, and maintaining the systems that inventors use to make and emplace operations. They ensure that software moves easily from law to product without crimes, detainments, or failures.
Their main part is to integrate development and operations, enabling faster releases, better collaboration, and stable performance.
DevOps Engineers generally work with:
- CI/CD channels
- Cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Docker and Kubernetes
- Monitoring and logging tools
- Robotization scripts
- Structure as Code (Terraform, Ansible)
- Security and configuration operation
They ensure operations are scalable, effective, and constantly available.
Full Stack Developer vs DevOps Engineer – The Core Difference
Although both work in the software development lifecycle, their focus areas are different.
Full Stack Developers make operations
DevOps Engineers make systems that run operations
Full Stack Developers write the law and manage operation sense. DevOps Engineers ensure that law runs reliably in product.
In simpler terms:
Full Stack = Creates the product
DevOps = Delivers and maintains the product
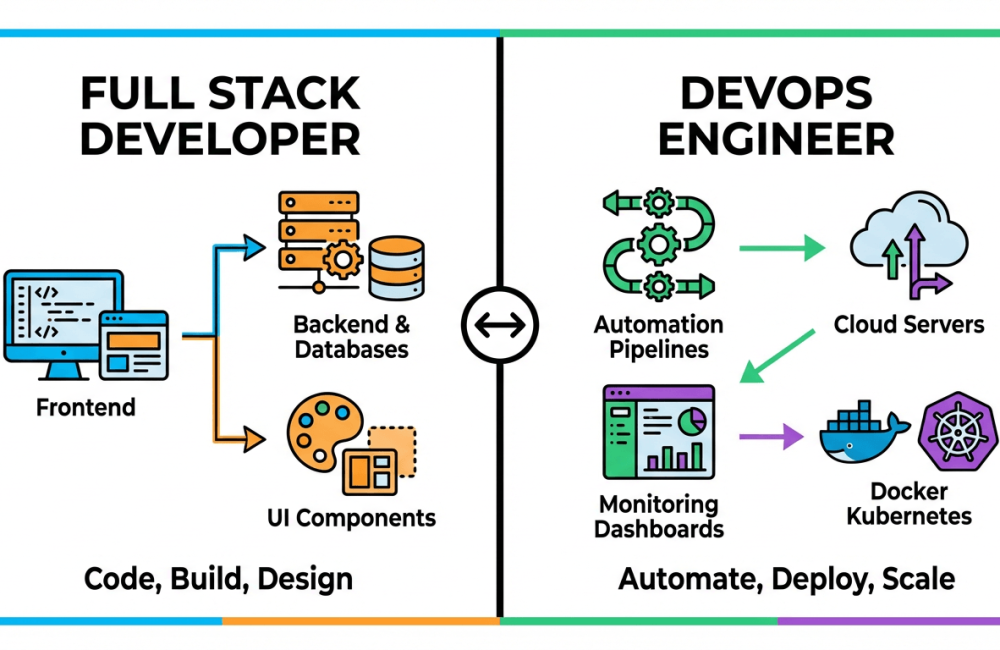
Full Stack Developer Responsibilities
- Develop UI and backend sense
- Integrate APIs
- Work with databases
- Write clean, applicable law
- Handle debugging
Unite with contrivers and other Developers
DevOps Engineer Responsibilities
- Automate deployment channels
- Examiner system health
- Manage pall structure
- Handle garçon configurations
- Ameliorate delivery speed
- Figure tools for Developers
Both places are important, but they concentrate on different stages of the development process.
Skills needed for Full Stack Developers
Full Stack Developers need a protean skill set because they work across the entire operation.
Common skills include:
- Understanding HTML, CSS, JavaScript
- Experience with frontend fabrics like React, Vue, or Angular
- Knowledge of backend languages (Node.js, Java, Python, PHP)
- Familiarity with REST APIs
- Experience with databases
- Interpretation control using Git
Full Stack Developers also profit from having problem-working chops and good communication capacities.
Skills needed for DevOps Engineers
DevOps is more focused on robotization, scalability, and trustability. Their chops revolve around structure, CI/CD, and pall operations.
Important DevOps skills include:
- CI/CD tools (Jenkins, GitHub conduct, GitLab CI)
- Containerization tools (Docker, Kubernetes)
- Cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Linux system administration
- Monitoring tools (Prometheus, Grafana)
- Structure as Code
- Networking basics
DevOps requires a strong mindset of robotization and system trustability.
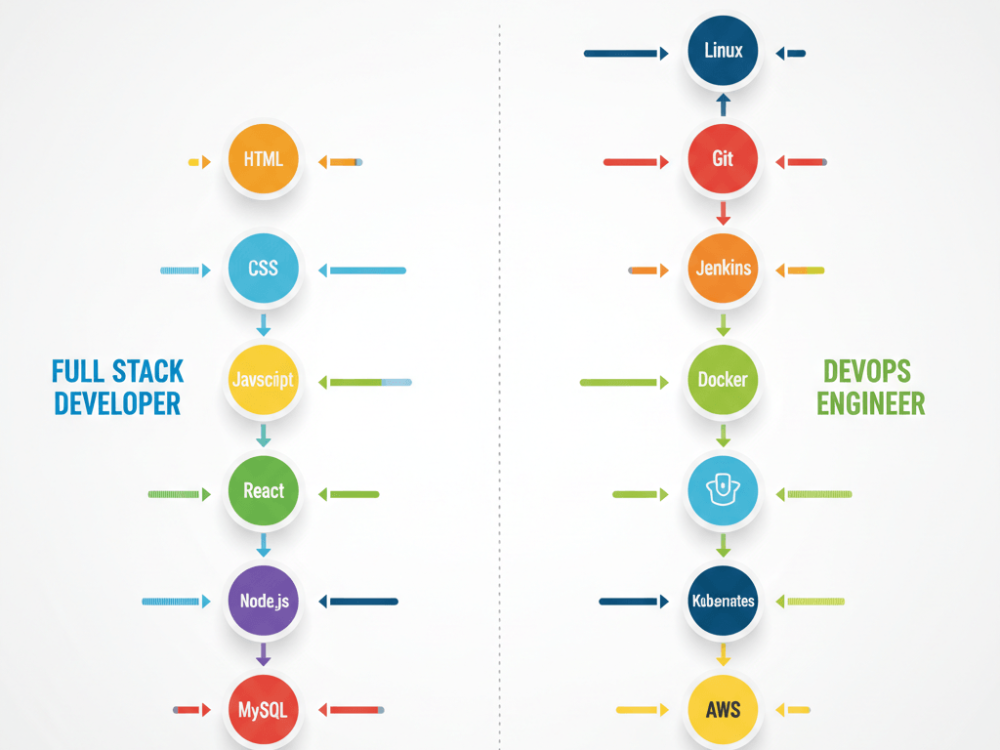
Learning Path: How to Come a Full Stack Developer
Full Stack development has a structured literacy trip. utmost newcomers start with the basics of web development before moving toward backend skills and advanced fabrics.
A typical literacy path looks like this:
1. Start with Frontend Basics
Learn HTML, CSS, and JavaScript fundamentals. This builds the foundation for any web-grounded full stack part.
2. Learn a Frontend Framework
React and Angular are the most popular choices. They help you make interactive and fast stoner interfaces.
3. Learn Backend Development
Choose a backend language like Node.js, Python, or Java.
Understand routing, authentication, business sense, and CRUD operations.
4. Understand Databases
Learn SQL databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL) and NoSQL (MongoDB).
5. Build Real Applications
Exercise with systems like e-commerce apps, dashboards, or reserving systems.
6. Learn Deployment Basics
Full Stack Developers must understand at least introductory deployment to Cloud platforms like AWS EC2, Vercel, or Netlify.
Learning Path: How to Come a DevOps Engineer
DevOps has a veritably different literacy trip concentrated on systems, robotization, and structure.
1. Learn Linux Fundamentals
utmost DevOps tools and systems run on Linux surroundings.
2. Understand Version Control
Git is essential for DevOps because robotization relies on it.
3. Learn CI/CD Tools
Start with Jenkins or GitHub conduct. Understand how channels automate deployment.
4. Learn Containerization
Docker is the base. Kubernetes is the advanced step.
5. Explore Cloud Platforms
The utmost companies use AWS, followed by Azure and Google Cloud.
Start with EC2, S3, IAM, and VPC basics.
6. Learn structure as Code
Terraform and Ansible help automate structure.
7. Understand Monitoring & Logging
Tools like Grafana, Prometheus, and ELK help maintain system health.
Career Scope and openings
Both places are in high demand, but the type of companies hiring them varies.
Full Stack Developer Career Scope
Full Stack Developers work in:
- Startups
- IT companies
- Product-grounded companies
- Web development agencies
They’re valued because they can handle both frontend and backend tasks.
DevOps Engineer Career Scope
DevOps Engineers are largely in demand in:
- Cloud companies
- SaaS companies
- Robotization-grounded organisations
- Large-scale enterprises
Companies calculate on DevOps to ameliorate delivery speed and reduce time-out.
Salary Comparison (India)
Hires vary based on experience, company size, and skill situations.
Full Stack Developer payment (India)
- Entry position: ₹3.5 – ₹5 LPA
- Mid-level: ₹6 – ₹12 LPA
- Elderly position: ₹12 – ₹20 LPA
DevOps Engineer payment (India)
- Entry position: ₹5 – ₹7 LPA
- Mid-level: ₹8 – ₹15 LPA
- Elderly position: ₹15 – ₹30 LPA
DevOps generally pays advanced because it requires deeper structure knowledge.
Conclusion
Choosing between becoming a Full Stack Developer or a DevOps Engineer depends entirely on your interests, strengths, and long-term career goals. Both roles play a critical part in modern software development — one focuses on building applications, while the other ensures those applications run smoothly, securely, and efficiently.
At APEC Training, we help students gain the right skills, confidence, and real-world exposure to excel in both fields. Whether you want to master Full Stack Development or step into the high-demand world of DevOps, our industry-driven courses, hands-on projects, and expert trainers guide you every step of the way.
If you’re ready to build a strong IT career and explore the best opportunities in the tech industry, APEC Training is the right place to start your journey.




